Properties of electrical signals
An
electrical signal is a voltage or current which conveys information, usually it
means a voltage. The term can be used for any voltage or current in a circuit.
The
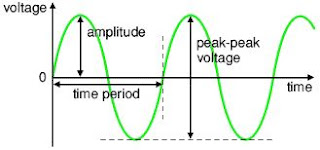
diagram shows a sine wave but these properties apply to any
signal with a constant shape.
The voltage-time graph
on the right shows various properties of an electrical signal
Amplitude is the maximum
voltage reached by the signal.
It is measured in volts, V.
It is measured in volts, V.
Peak voltage is another name for amplitude.
Peak-peak voltage is twice the peak
voltage (amplitude). When reading an oscilloscope trace it is usual to measure
peak-peak voltage.
Time period is the time taken for the signal to complete one
cycle.
It is measured in seconds (s).
It is measured in seconds (s).
But
time periods tend to be short so milliseconds (ms) and microseconds
(µs) are often used. 1ms = 0.001s and
1µs = 0.000001s.
Frequency is the number of
cycles per second.
It is measured in hertz (Hz), but frequencies tend to be high so kilohertz (kHz) and megahertz (MHz) are often used. 1kHz = 1000Hz and 1MHz = 1000000Hz.
|
frequency =
|
1
|
and
|
time period =
|
1
|
|
time
period
|
frequency
|
Mains
electricity in the BANGLADESH has a frequency of 50Hz,
so it has a time period of 1/50 = 0.02s = 20ms.
so it has a time period of 1/50 = 0.02s = 20ms.
No comments:
Post a Comment